M1A2 Abrams Main Battle Tank
The mission of the M1A2 Abrams tank is to close with and destroy enemy forces using firepower, maneuver, and shock effect. The M1A2 is being fielded to armor battalions and cavalry squadrons of the heavy force. In lieu of new production, the Army is upgrading approximately 1,000 older M1 tanks to the M1A2 configuration. During the Army's current M1A2 procurement program about 1,000 older, less capable M1 series tanks will be upgraded to the M1A2 configuration and fielded to the active forces. There is currently no plan to field the M1A2 to the ARNG. The Army has procured 62 new tanks in the A2 configuration and as of early 1997 completed the conversion of 368 older M1s to M1A2s. An additional 580 M1s are being upgraded to A2s under a five-year contract awarded in FY 1996, with a total of 998 M1 upgrades planned. In FY 1999, the Army will begin upgrading M1s to the M1A2 System Enhancement Program (SEP) configuration. This sensor also will be added to older M1A2s starting in FY 2001. When the SEP enters production, the Army will have a total of 627 M1A2s, all of which will eventually be converted to the SEP configuration.
Further M1A2 improvements, called the System Enhancement Program (SEP), are underway to enhance the tank's digital command and control capabilities and to to improve the tank's fightability and lethality. The M1A2 SEP (System Enhancement Package), is the digital battlefield centerpiece for Army XXI. It is the heavy force vehicle
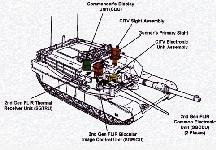
that will lead Armor into the next century and transition the close combat mission to the Future Combat System (FCS). The M1A2 SEP is an improved version of the M1A2. It contains numerous improvements in command and control, lethality and reliability. M1A2 SEP is in final operational testing, and scheduled to start fielding in 2000. M1A2 SEP tanks are scheduled to begin fielding in 3QFY00. The M1A2 System Enhanced Program (SEP) is an upgrade to the computer core that is the essence of the M1A2 tank. The SEP upgrade includes improved processors, color and high resolution flat panel displays, increased memory capacity, user friendly Soldier Machine Interface (SMI) and an open operating system that will allow for future growth. Major improvements include the integration of the Second Generation Forward Looking Infared (2nd Gen FLIR) sight, the Under Armor Auxiliary Power Unit (UAAPU) and a Thermal Management System (TMS).
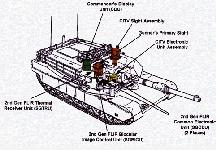 The 2nd Generation Forward Looking InfraRed sighting system (2nd Gen FLIR) will replace the existing Thermal Image System (TIS) and the Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer. The incorporation of 2nd Gen FLIR into the M1A2 tank will require replacement of all 1st Gen FLIR components. From the warfighter perspective, this is one of the key improvements on the SEP. The 2nd Gen FLIR is a fully integrated engagement-sighting system designed to provide the gunner and tank commander with significantly improved day and night target acquisition and engagement capability. This system allows 70% better acquisition, 45% quicker firing and greater accuracy. In addition, a gain of 30% greater range for target acquisition and identification will increase lethality and lessen fratricide. The Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer (CITV) provides a hunter killer capability. The 2nd GEN FLIR is a variable power sighting system ranging from 3 or 6 power (wide field of view) for target acquisition and 13, 25 or 50 power (narrow field of view) for engaging targets at appropriate range.
The 2nd Generation Forward Looking InfraRed sighting system (2nd Gen FLIR) will replace the existing Thermal Image System (TIS) and the Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer. The incorporation of 2nd Gen FLIR into the M1A2 tank will require replacement of all 1st Gen FLIR components. From the warfighter perspective, this is one of the key improvements on the SEP. The 2nd Gen FLIR is a fully integrated engagement-sighting system designed to provide the gunner and tank commander with significantly improved day and night target acquisition and engagement capability. This system allows 70% better acquisition, 45% quicker firing and greater accuracy. In addition, a gain of 30% greater range for target acquisition and identification will increase lethality and lessen fratricide. The Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer (CITV) provides a hunter killer capability. The 2nd GEN FLIR is a variable power sighting system ranging from 3 or 6 power (wide field of view) for target acquisition and 13, 25 or 50 power (narrow field of view) for engaging targets at appropriate range.
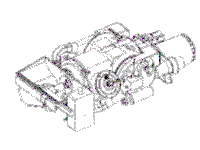
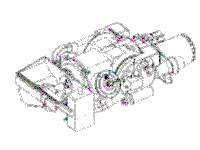 The UAAPU consist of a turbine engine, a generator, and a hydraulic pump. The generator is capable of producing 6 Kilowatts of electrical power at 214 Amps, 28 vdc, and the hydraulic pump is capable of delivering 10 Kilowatts of hydraulic power. The UAAPU can meet the electrical and hydraulic power to operate all electronic and hydraulic components used during mounted surveilance operations and charge the tank's main batteries. The UAAPU will reduce Operational and Support cost by utilizing the same fuel as the tank at a reduced rate of 3-5 gallons per operational hour. The UAAPU is mounted on the left rear sponson fuel cell area and weighs 510 pounds.
The UAAPU consist of a turbine engine, a generator, and a hydraulic pump. The generator is capable of producing 6 Kilowatts of electrical power at 214 Amps, 28 vdc, and the hydraulic pump is capable of delivering 10 Kilowatts of hydraulic power. The UAAPU can meet the electrical and hydraulic power to operate all electronic and hydraulic components used during mounted surveilance operations and charge the tank's main batteries. The UAAPU will reduce Operational and Support cost by utilizing the same fuel as the tank at a reduced rate of 3-5 gallons per operational hour. The UAAPU is mounted on the left rear sponson fuel cell area and weighs 510 pounds.
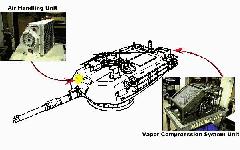
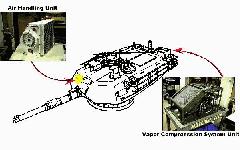 Another improvement in the M1A2 SEP is the Thermal Management System (TMS) which keeps the temperature within the crew compartment under 95 degrees and the touch temperature of electronic units under 125 degrees during extreme conditions. By reducing the temperature in the crew compartment for the crew and electronic units, this increases the operational capability for both soldiers and the vehicle. The TMS consists of an Air Handling Unit (AHU) and a Vapor Compression System Unit (VCSU) capable of providing 7.5 Kilowatts of cooling capacity for the crew and Line Repairable Units (LRUs). The AHU is mounted in the turret bustle and the VCSU is mounted forward of the Gunner's Primary Sight (GPS). The TMS uses enviromentally friendly R134a refrigerant and propylene glycol/water mixture to maintain the LRU touch temperature at less than 140 degrees Fahrenheit. The TMS is mounted in the left side of turret bussel and weighs 384 pounds.
Another improvement in the M1A2 SEP is the Thermal Management System (TMS) which keeps the temperature within the crew compartment under 95 degrees and the touch temperature of electronic units under 125 degrees during extreme conditions. By reducing the temperature in the crew compartment for the crew and electronic units, this increases the operational capability for both soldiers and the vehicle. The TMS consists of an Air Handling Unit (AHU) and a Vapor Compression System Unit (VCSU) capable of providing 7.5 Kilowatts of cooling capacity for the crew and Line Repairable Units (LRUs). The AHU is mounted in the turret bustle and the VCSU is mounted forward of the Gunner's Primary Sight (GPS). The TMS uses enviromentally friendly R134a refrigerant and propylene glycol/water mixture to maintain the LRU touch temperature at less than 140 degrees Fahrenheit. The TMS is mounted in the left side of turret bussel and weighs 384 pounds.
The Army requires that all systems operate in the Army Common Operating Environment (ACOE) to improve combined arms operations. Digitization and information dominance across the entire Army for tactical elements is accomplished using Force XXI Battle Command for Brigade and Below (FBCB2) software. In Abrams, FBCB2 software is hosted on a separate card that enables situational awareness across the entire spectrum of tactical operation. It improves message flow, through 34 joint variable message formats, reports ranging from contact reports to logistic roll ups, as well as automatically providing vehicle location to friendly systems. The SEP allows for digital data dissemination with improved ability to optimize information based operations and maintain a relevant common picture while executing Force XXI full dimensional operation. This enhancement increases capability to control the battlefield tempo while improving lethality and survivability. Finally to ensure crew proficiency is maintained, each Armor Battalion is fielded an improved Advanced Gunnery Training System (AGTS) with state-of-the-art graphics.
Changes to the M1A2 Abrams Tank contained in the System Enhancement Program (SEP) and "M1A2 Tank FY 2000" configuration are intended to improve lethality, survivability, mobility, sustainability and provide increased situational awareness and command & control enhancements necessary to provide information superiority to the dominant maneuver force. The Abrams Tank and the Bradley Fighting Vehicle are two central components of the dominant maneuver digital force.
System Enhancement Program upgrades are intended to:
- improve target detection, recognition and identification with the addition of two 2nd generation FLIRs.
- incorporate an under armor auxiliary power unit to power the tank and sensor suites.
- incorporate a thermal management system to provide crew and electronics cooling.
- increase memory and processor speeds and provide full color map capability.
- provide compatibility with the Army Command and Control Architecture to ensure the ability to share command & control and situational awareness with all components of the combined arms team.
Additional weight reduction, embedded battle command, survivability enhancement, signature management, safety improvement, and product upgrade modifications to the M1A2 will comprise the "M1A2 Tank FY 2000" configuration fielded to units of the digital division beginning in FY 2000.
The M1A2 IOT&E was conducted from September-December 1993 at Fort Hood , TX and consisted of a gunnery phase and a maneuver phase. The Director determined that the test was adequate, the M1A2 was operationally effective, but not operationally suitable and unsafe. That assessment was based on poor availability and reliability of the tank, instances of the uncommanded tube and turret movement, inadvertent .50 caliber machine gun firing, and hot surfaces which caused contact burns.
FOT&E #1 was conducted in September-October 1995 in conjunction with the New Equipment Training for two battalion sized units. Despite assurances from the Army that all corrective actions were applied, numerous instances of uncommanded tube and turret movement, Commander's Independent Display (CID) lockup and contact burns continued during FOT&E #1. The follow-on test was placed on hold and the Army "deadlined" the two battalions of M1A2 tanks at Fort Hood for safety reasons. The PM isolated 30 "root causes" of the safety problems and completed hardware and software upgrades in June 1996 which were assessed in FOT&E #2.
The M1A2 TEMP was approved during 2QFY98. This TEMP includes a coordinated plan for FOT&E #3 of the M1A2 in conjunction with the IOT&E of the Bradley Fighting Vehicle in FY99 at Fort Hood , TX . This combined operational test will consist of 16 force-on-force battles between a Bradley Fighting Vehicle System-A3/M1A2 SEP combined arms team and M1A1/ Bradley-ODS combined arms team. Additionally, it will serve as the operational test for the 2d Generation FLIR. This approach implements the Secretary of Defense theme of combining testing in order to save resources and ensure a more realistic operational environment.
The Army and DOT&E completed vulnerability assessment efforts and concluded that the "M1A2 Tank FY 2000" is a significant change from the original M1A2 design and will require a system-level survivability evaluation. This evaluation will rely on full-up system level testing of two systems, component and sub-system level testing, modeling and simulation, existing data, and previous testing to assess susceptibility and vulnerability of the "M1A2 Tank FY 2000" and its crew to the expected threat and to assess battle damage repair capabilities.
The M1A2 Abrams Tank with the corrective actions applied by the Program Manager during FY96 is assessed to be operationally effective and suitable. The availability, reliability, fuel consumption, and safety problems observed in previous testing have been corrected. FOT&E #2 was adequately conducted in accordance with approved test plans and the Abrams TEMP. There were no observed instances of the uncommanded tube and turret movement, inadvertent .50 caliber machine gun firing, and hot surfaces which caused contact burns in previous testing.
The largest area of technical risk to the program is the development of the Embedded Battle Command software which is intended to provide friendly and enemy situational awareness and shared command & control information throughout the combined arms team. This software is being developed as a Horizontal Technology Insertion program and will be provided to the weapon systems and C2 nodes of the combined arms team in FY00. This development schedule is high risk and could adversely impact the M1A2 schedule.











Operations and Support
While the M1A2 SEP and M1A1D provide improved combat capabilities overmatch; the Army is working to improve reliability, reduce logistical footprint, and lower Operations and Support [O&S] costs for the tank. This effort is focused on two initiatives that provide the force with the biggest "bang for the buck" in terms of O&S cost reduction, readiness improvement, and sustainment of combat overmatch. These initiatives include the following Abrams Engine Campaign and the Abrams Integrated Management Overhaul Program (AIM):
. The AGT 1500 engine has served the Abrams tank well. It afforded a significant combat edge due to its lightweight, power, and stealth. However, the AGT 1500 is getting old and the fleet faces problems in maintaining this workhorse. The AGT 1500 represents 1960s technology and has been out of production since 1992. Declining reliability causes the engine to account for around 64% of the Abrams tank reparable O&S costs. The Army is focusing on the engine as a major element in easing the maintenance burden for the force while substantially reducing O&S costs.
PM Abrams has developed a two-phased program to improve engine readiness and lower costs. The first phase makes innovative use of a partnership with PM/AMC/industry to overhaul the existing AGT 1500 engine/components. This program is termed PROSE (Partnership for Reduced O&S Costs, Engine). Under PROSE, the government will "team" with the original equipment manufacturer to reengineer the production process and improve field support. The contractor provides quality parts and expert technical support, and the government (our depots) provides the skilled labor and facilities.
The second phase of the engine initiative involves replacing the AGT 1500 engine with a new engine. There is great potential for improved tank readiness and long term O&S cost reduction in the implementation of this phase. This approach will not be cheap and will require a major decision by the Army. A 2 billion-dollar investment is required to replace the current engine with a new engine in the active component along, with a potential savings of 13 billion over the remaining life of the tank.
The PROSE process is expected to improve reliability by 30%. The benefits of the new engine are much more dramatic - the Army could achieve a 4-5 fold improvement in reliability, hopefully a 35% reduction in fuel consumption, a 42% reduction in the number of parts, and a 15-20% improvement in vehicle mobility. Life cycle engine O&S costs are projected to drop from 16 billion dollars over 30 years with the current engine to 3 billion dollars with the new engine.
The second piece of our O&S cost reduction strategy is the Abrams Integrated Management (AIM) program. The AIM process overhauls an old M1A1 tank to original factory standards, applying all applicable MWO's. The AIM Proof of Principle was completed in 1997, proving the cost-effectiveness of the concept and helping to define the scope. The AIM tank demonstrated an 18% O&S cost savings when compared to non-AIM tanks. The AIM overhaul concept is a cost-effective solution to address the problems of rising tank sustainment costs and increasing readiness concerns.
 The 2nd Generation Forward Looking InfraRed sighting system (2nd Gen FLIR) will replace the existing Thermal Image System (TIS) and the Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer. The incorporation of 2nd Gen FLIR into the M1A2 tank will require replacement of all 1st Gen FLIR components. From the warfighter perspective, this is one of the key improvements on the SEP. The 2nd Gen FLIR is a fully integrated engagement-sighting system designed to provide the gunner and tank commander with significantly improved day and night target acquisition and engagement capability. This system allows 70% better acquisition, 45% quicker firing and greater accuracy. In addition, a gain of 30% greater range for target acquisition and identification will increase lethality and lessen fratricide. The Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer (CITV) provides a hunter killer capability. The 2nd GEN FLIR is a variable power sighting system ranging from 3 or 6 power (wide field of view) for target acquisition and 13, 25 or 50 power (narrow field of view) for engaging targets at appropriate range.
The 2nd Generation Forward Looking InfraRed sighting system (2nd Gen FLIR) will replace the existing Thermal Image System (TIS) and the Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer. The incorporation of 2nd Gen FLIR into the M1A2 tank will require replacement of all 1st Gen FLIR components. From the warfighter perspective, this is one of the key improvements on the SEP. The 2nd Gen FLIR is a fully integrated engagement-sighting system designed to provide the gunner and tank commander with significantly improved day and night target acquisition and engagement capability. This system allows 70% better acquisition, 45% quicker firing and greater accuracy. In addition, a gain of 30% greater range for target acquisition and identification will increase lethality and lessen fratricide. The Commander's Independent Thermal Viewer (CITV) provides a hunter killer capability. The 2nd GEN FLIR is a variable power sighting system ranging from 3 or 6 power (wide field of view) for target acquisition and 13, 25 or 50 power (narrow field of view) for engaging targets at appropriate range. 















